top
Welcome to Weiqi Yin's webpage!
| FEA | |
| MSC.Software | |
| Abaqus | |
| Ansys/Ls-Dyna | |
| COMSOL | |
| Experimental | |
| CAD | |
| SolidWorks | |
| Pro/Engineering | |
| Catia | |
| AutoCAD | |
MSC.Software |
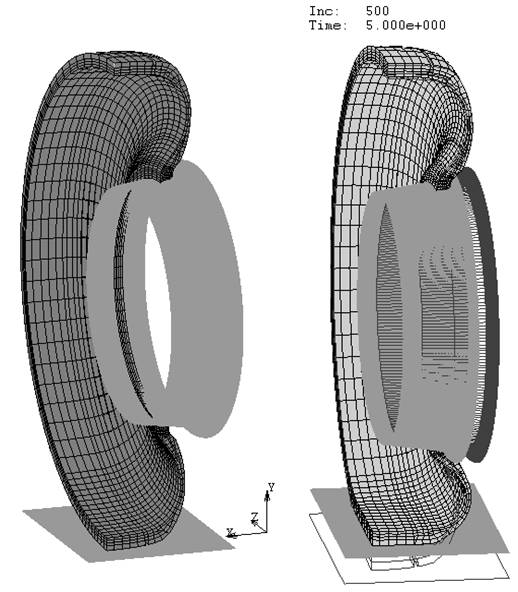
Static analysis of radial tires |
Radial tire is a complex composite composed of rubber and cord-rubber composite. It is one of the most important parts applied in the automobile. The mechanical characteristics of the tire have significant effects on the performances of the automobile. In recent years, the finite element method has been widely applied in the design and development of radial tires. It can be used to replace many experiments, to shorten the research and development process of a new type of tire, to enhance the design level and improve the quality of tire, and to get rid of the traditional empirical and semiempirical design. In this thesis, the nonlinear finite element static models of four radial tires have been built by using MSC.Marc software. It can be used to analyze the displacements, strains and stresses of these tires under loading cases of free-rotation and statically contacting with road, and to obtain the footprint of the tire in the contacted areas. The axisymmetrical model has been applied to simulate the processes including assemblage of rim, inflating and free-rotation, while the 3D one-quarter-tire model has been applied to simulate the processes including assemblage of rim, inflating and vertical-loading. These models for static analysis have considered the geometrical complexity of the tire structure, the special features of the materials, including the nonlinearity and incompressibility of the rubber material, together with the nonlinearity of the large deformation of the tire and the nonlinear contact boundary conditions. In these analyses the Mooney-Rivlin model is adopted as the constitutive relations of the rubber material. The cord-rubber composites, such as belt, body ply and bead are simulated by rebar models. For simplicity, the direct restriction approach has been applied to deal with the contact conditions between the tire and rim, and the rim and road have been simplified as rigid bodies.
|
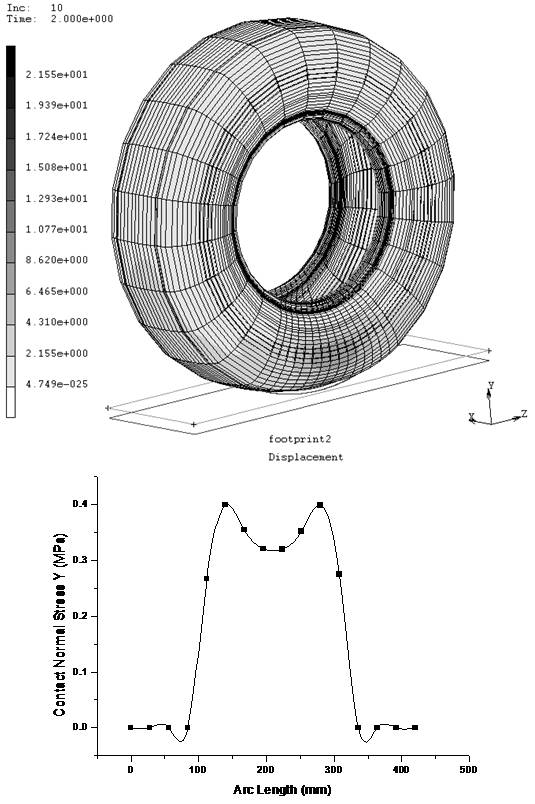
Dynamic analysis of radial tires |
The static analysis of tire is not enough because the tire is developed to roll on the road when mounted on the automobile. Based on the static analysis, two steady-state rolling models of radial tires have been built. Using these models the distributions of the contact and friction stresses on the contacted area between the tire and the road have been obtained for the loading cases of full braking, full traction and free rolling. The relationships between the traction and spinning velocity and between the cornering force and the cornering velocity have been obtained as well.
|
Abaqus |
Residual stress characterization of plain woven textile composite |
To predict the corresponding residual stresses of plain woven textile composites, finite element model can be used to simulate the complex geometry of textile composites. The geometry shape of the FE model for the representative volume element (RVE) as shown. The real dimensions were measured via digital caliper along with the assistance of microscope. Parametric modeling using Pro/Engineering is used to construct the 3-D structure, which can better simulate the geometry of textile and easily adjust the geometry. By this way, the dimension of the geometry structure can be easily modified to make it close to the real dimension. The CAD file is imported into Abaqus software separately and assembled together. Contact condition between fiber and matrix is defined as glued together under the assumption that no slipping occurring between them.
|
Crash simulation between bumper and rigid wall |
Ansys/Ls-Dyna |
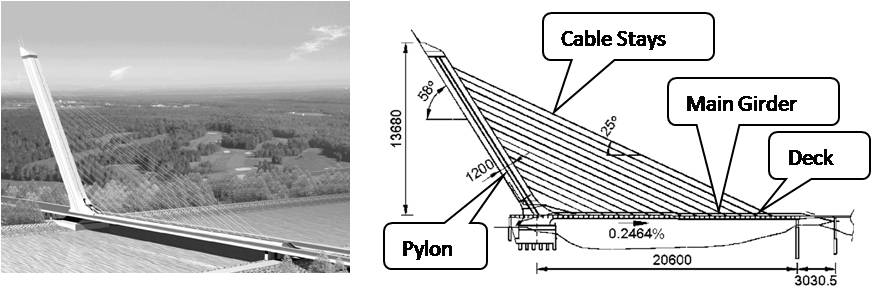
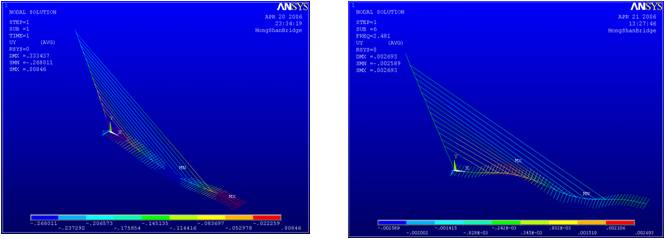
Static & Dynamic Study of Hongshan Cable-Stayed Bridge |
This report presents the static and dynamic study of a harp-shaped single span cable-stayed bridge, Hongshan Bridge, located in Changsha, Hunan Province, China. In this report, ANSYS is used to do a static analysis and a modal analysis of the bridge separately to obtain the static and dynamic characteristics of the bridge. 3D elastic Beam and bilinear line elements are introduced and used to simulate the main parts of the bridge. At the same time, some reasonable simplifications and assumptions are addressed to make it easier to construct the FE model.
|
COMSOL FemLab |
Moire Interferometry |
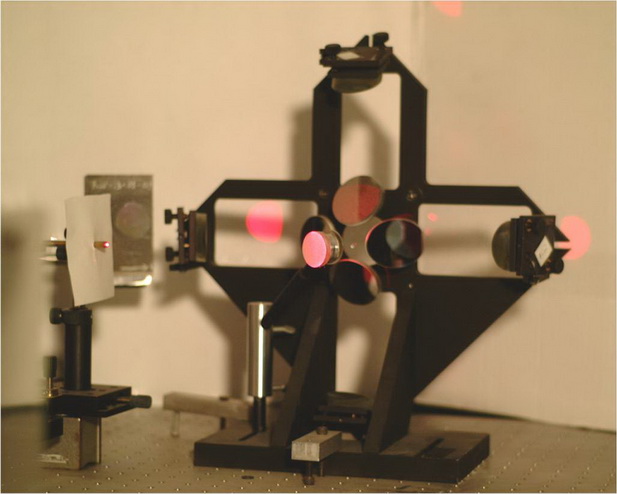
Moiré interferometry is a laser-based optical technique that combines the concepts of optical interferometry and geometrical moiré. It has been widely applied for studies of composite materials, fracture mechanics, electronic packages, etc. because of its full-field displacement measurement capability, high displacement sensitivity, high spatial resolution, and high signal to noise ratio. It is a non-contacting and whole-field method capable of measuring both normal and shear strain. A schematic of the moiré interferometry setup can be seen in Figure 1-1. Figure 1-2 shows one actual four-beam Moiré interferometer with a specimen placed in front of it.
Four-beam Moiré Interferometer schematic
Four-beam Moiré Interferometer |
Residual stress characterization of plain woven textile composite |
Residual stresses within composites come from the requirement of high temperature heating cycle during the manufacturing process. Those high temperatures are required so that the resin can fully heat and complete its polymerization process as well as wet the fibers and finally cure into a hard structure. This necessary process introduces a significant amount of residual stresses into the composite specimen after the heating cycle completes and the specimen cools down to room temperature. The residual stresses in composites arise from both chemical and thermal shrinkage. The chemical shrinkage is due to polymerization of the resin in which the two monomers in the epoxy come together to form the final compound. The majority of the chemical shrinkage occurs during the initial heating period of the curing cycle and therefore does not contribute to the overall residual stresses. This is because stresses cannot exist before the composite fully cures and the resin transforms to the solid state. However, there is some additional chemical shrinkage that does contribute to the final residual stress levels in the specimen that occurs after the solidification of the resin. On the ply level, a significant amount of the residual stresses develop because of the mismatch that naturally exists between the coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE) of the two materials. The resin typically has a much higher CTE value than the fiber; therefore a large amount of thermally induced shrinkage would develop in the matrix. However, the higher stiffness fibers restrict the contraction of the matrix. That restriction is what introduces the residual stresses into the composite.
|
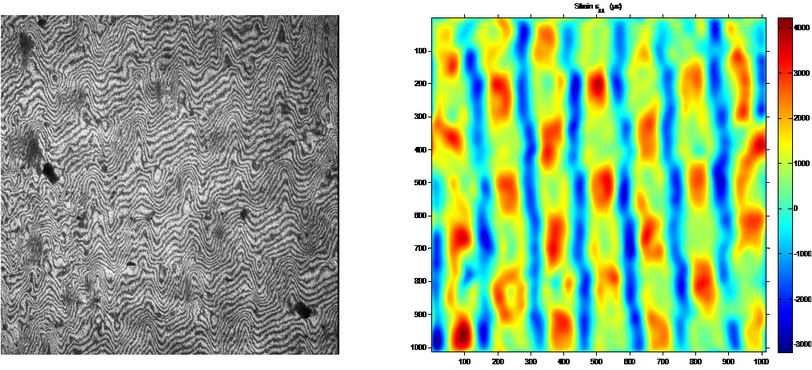
Shrinkage measurement of concrete material |
Shrinkage is one of the fundamental characteristics of concrete which mainly results from moisture diffusion and self-desiccation. Moreover, shrinkage depends on many factors, such as water/cement ratio, surrounding relative humidity and temperature, aggregate quantity, and the size and shape of specimen. This crucial characteristic influences the development of stress and induces subsequent cracking of concrete. In order to better assess the structural life of concrete, the shrinkage, which is also time-dependent, must be measured in different drying conditions.
|
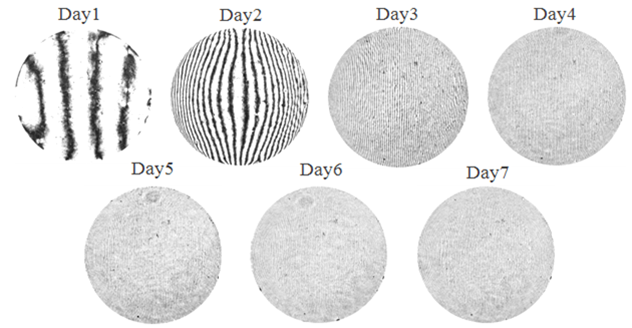
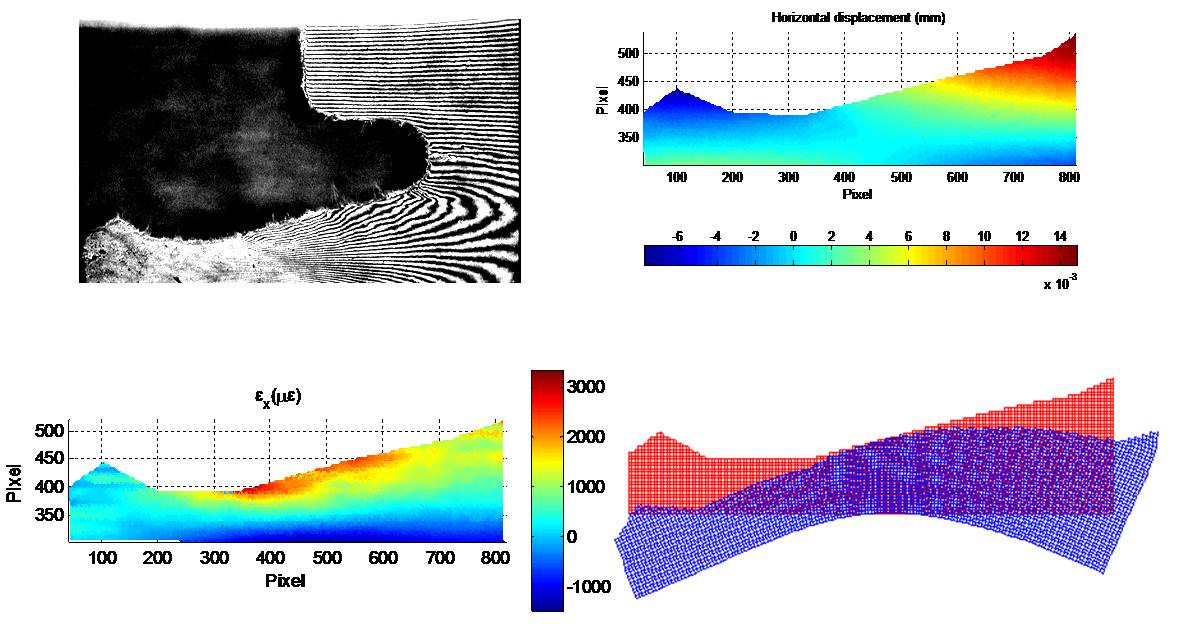
Assembly behavior measurement of laminate flooring system |
Laminate floor is a composite material made to look like natural products such as wood or natural stone. To understand the behavior of the laminate flooring system during the assembly process, tests on the samples are performed using moiré Interferometry which can determine the in-plane strain with very high accuracy even though the deformation is tiny.
|
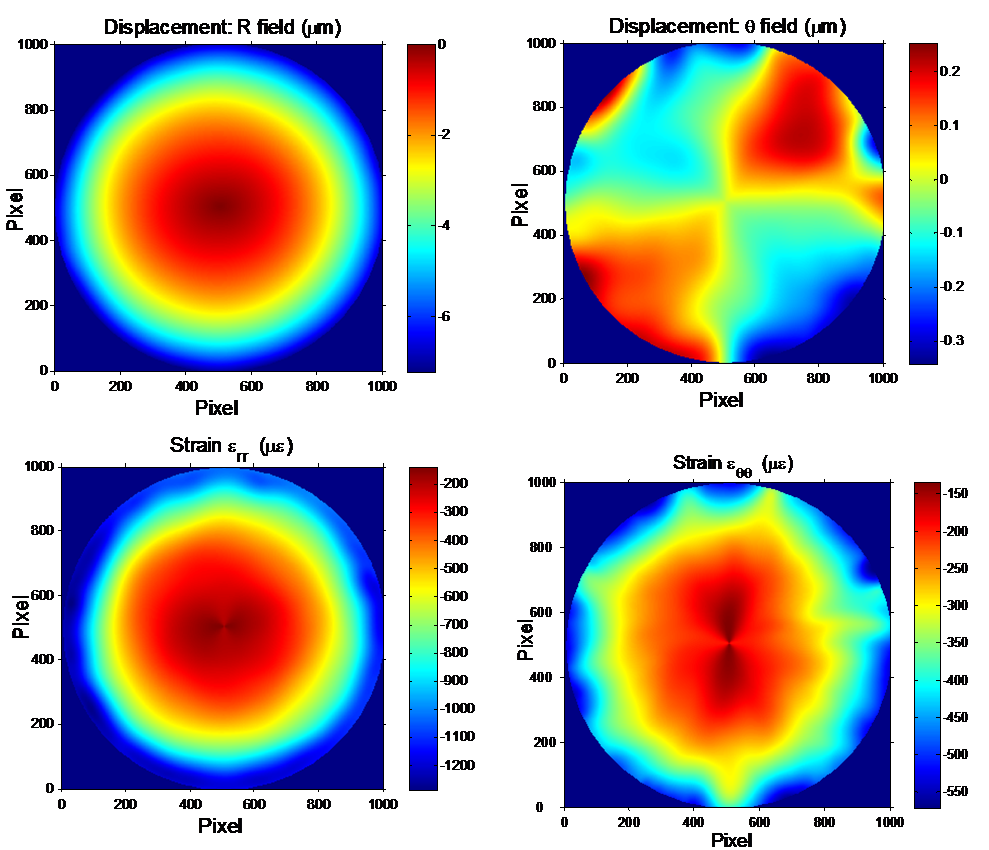
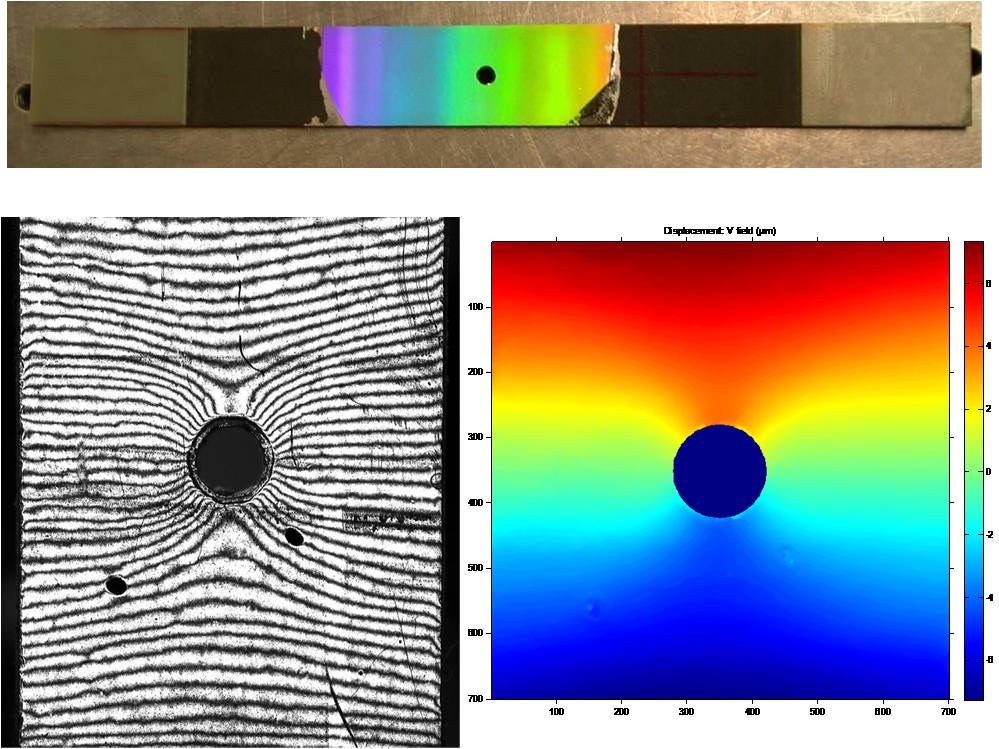
Material property identification of laminate plate |
The objective is to use Bayesian identification to for identification of the four ply-elastic constants from the full field displacement measurements on a laminate plate with a hole. The interest of identifying ply properties is that it allows to obtain both the extensional and the bending stiffnesses of the laminate. Due however to the varying sensitivity of the strain and displacement fields to the different ply properties, it is of primary importance to estimate the uncertainty with which these properties are identified. The Bayesian approach developed by Gogu will allow us to do this by taking into account the physics of the problem (i.e. the different sensitivities of the fields to the different properties), measurement uncertainty as well as uncertainty on other input parameters to the model such as the specimen geometry.
|
Digital Image Correlation (DIC) |
Digital image correlation (DIC) techniques have been increasing in popularity, especially in micro- and nano-scale mechanical testing applications due to its relative ease of implementation and use. Advances in digital imaging have been the enabling technology for this method and while white-light optics has been the predominate approach, DIC has recently been extended to SEM and AFM. Above and beyond the ability of image-based methods to provide a “box-seat” to the events that are occurring during deformation, these techniques have been applied to the testing of many materials systems because it offers a full-field description and is relatively robust at tracking a wide range of “markers” and varying surface contrast. The appeal of these image-based techniques, coupled with the lack of flexibility and prohibitive cost of commercial DIC software packages, provided the impetus for the development of a custom in-house software suite using the mathematical package MATLAB as the engine for calculations. This resulted in an open-source package that was uploaded to the public domain in an effort to provide free tools to users, but also to generate feedback for potential improvements and addition to the code. As such, a brief discussion of the primary features and methodology of this technique, along with some background on DIC and peak tracking will be presented here. DIC for strain measurement constitutes a major field of research and is followed by a healthy, vigorous, and dynamic discussion and discourse, so it is not the author’s intention to provide an exhaustive survey of the field. Instead, a more focused description of the tools required to make accurate measurements that provide insight on the deformation mechanisms that govern plasticity in nc-Al thin films is given. |
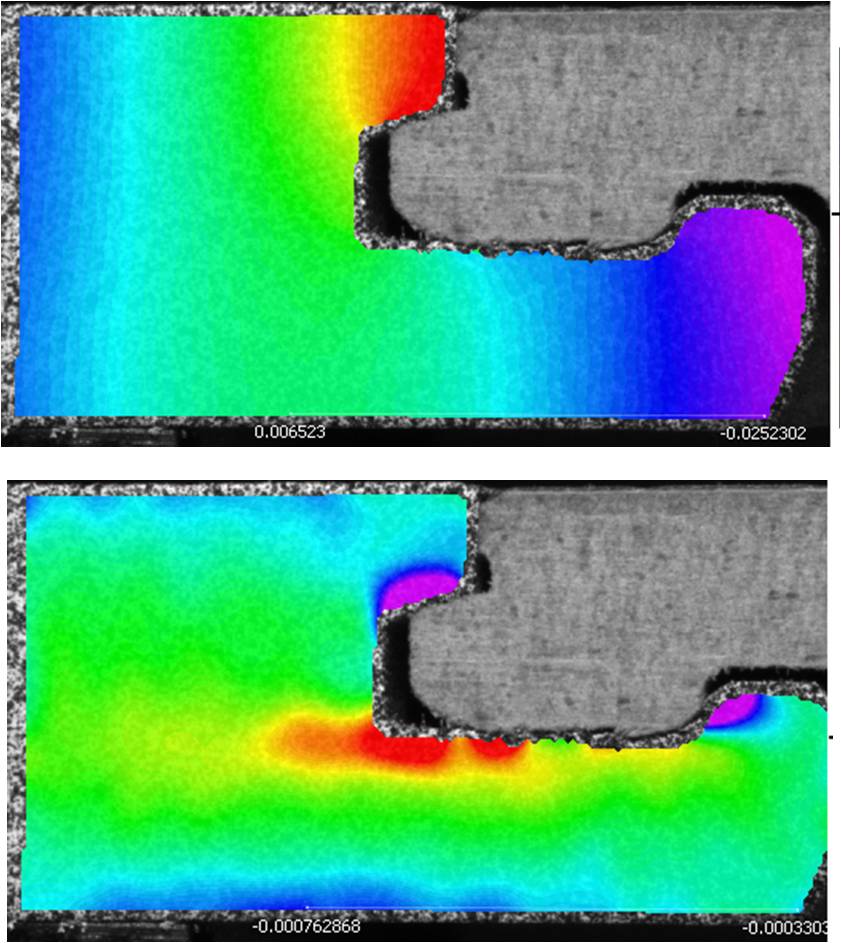
Assembly behavior measurement of laminate flooring system |
|---|
Laminate floor is a composite material made to look like natural products such as wood or natural stone. To understand the behavior of the laminate flooring system during the assembly process, tests on the samples are performed using high resolution digital image correlation produced by correlatedsolutions which can determine the 3D deformation with very high accuracy even though the deformation is tiny.
|
Strain Gage |
| What's New? |
| My daughter, Claire Xiangling Yin, was born on July 11, 2009 at Shands hospital |
| Social |
| June 2007-Present Consultant of Friendship Association of Chinese Students and Scholars at UF Feb. 2007-Feb. 2008 Graduate Senator of Student Government at University of Florida June 2006-June 2007 President of Friendship Association of Chinese Students and Scholars at UF Feb. 2005 / Feb. 2007 Director/Producer of 2005 and 2007 Chinese New Year Show |
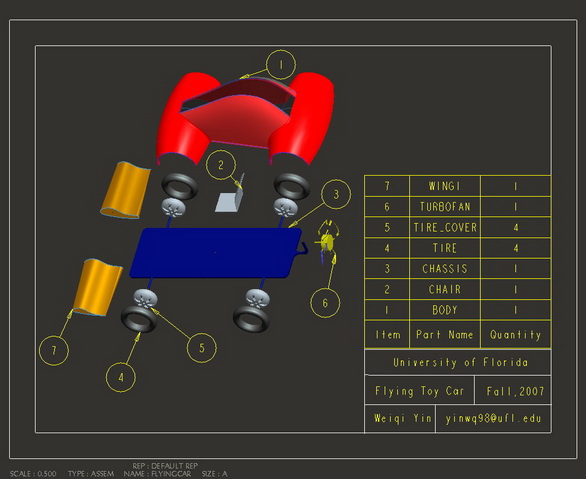
Pro/Engineering |
Flying toy car design |
|