http://www.mcg.edu/medart/Images/Art-Benion-Brasco.jpg
(Kabbani and Raghuveer, 2004)
Craniosynostosis is the term used to describe a developmental defect that affects the sutures and bones of the cranium. Craniosynostosis is basically the failure of differentiation between opposing cranial bone precursors leading to their coalescence into one bone and the failure to develop the suture that would normally appear between the bones (Barnes, 1994). Although craniosynostosis is usually described as premature suture fusion, sutural agenesis is a better term to describe some examples of craniosynostois because the suture never develops (Barnes, 1994). There are many permutations of sutural agenesis. Some occur as isolated field defects creating some asymmetry, while others are part of a polytropic syndrome that may have debilitating affects. There are over 150 craniosynostosis syndromes, however, Crouzon's disease and Apert's syndrome account for the majority (Kabbani and Raghuveer, 2004). There are mutliple descriptive terms used to categorize the shape of the cranium, Scaphocephaly, Brachycephaly, Plagiocephaly, Oxycephaly, and Trigonocephaly are the most common.
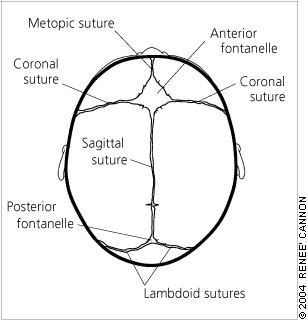
Diagram of normal cranium showing the vault sutures
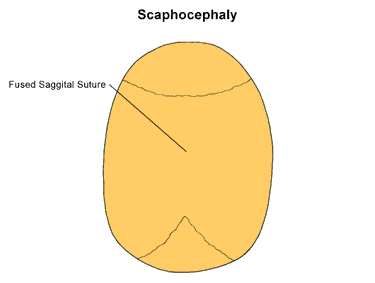
Scaphocephaly is the most common of the calvarial deformities associated with craniosynostosis (Kabbani and Raghuveer, 2004; David et al, 1982). The premature fusion of the sagittal suture elongates and narrows the cranium. Scaphocephaly usually occurs alone, however, it does occur somtimes in cases of Cruzon and Carpenter syndromes.
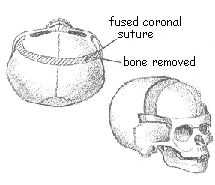
Brachycephaly refers to a short, wide cranium due to the bilateral involvement of the coronal suture
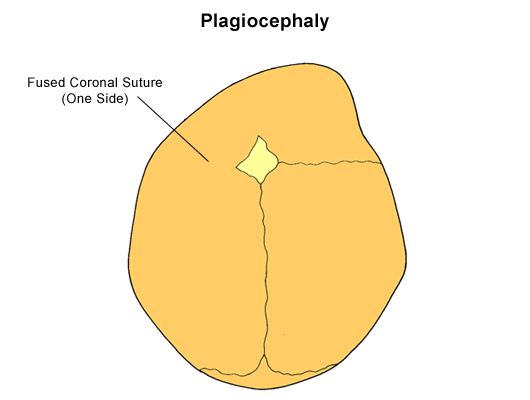
Plagiocephaly refers to cranial asymmetry created by localized clavarial recessions and compensatory bulges that may or may not be the effect of premature suture fusion (David et al, 1982). This deformity classified into three subgroups depending on the location and which sutures are involved. Frontal plagiocephaly is usually caused by the unilateral fusion on of the coronal suture and is characterized by unilateral flattening and recession of the lateral portion of the frontal bone and supraorbital ridge (David et al, 1982). Occipital plagiocephaly describes the flattening of the occipital region on one side, however, this deformity may or may not involve unilateral synostosis of the lambdoid suture and could be the result of mechanical forces (e.g., tendency to lie on one side, or car seat use) Hemicranial plagiocephaly is the most severe category of plagiocephaly and is the result of unilateral cranial growth delay with premature fusion of the coronal, squamosal, and lambdoid sutures in varying combinations (David et al, 1982) .
Oxycephaly describes a cranial shape that is high conical, its vertex appears pointed, and is the result of multiple suture fusion; there is no clear pattern to its manifestation (David et al, 1982).
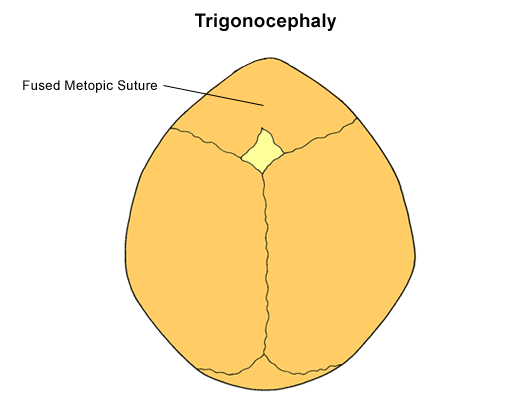
Trigonocephaly is a wedge-shaped deformity of the frontal bone with a bony ridge along the midline and is usually the result of metopic suture fusion (David et al, 1982).
Additional classification and common syndromes
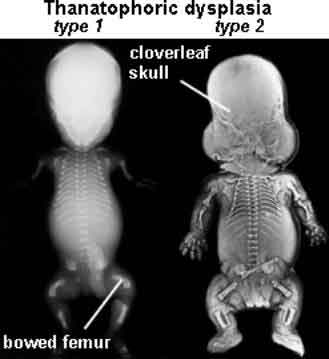
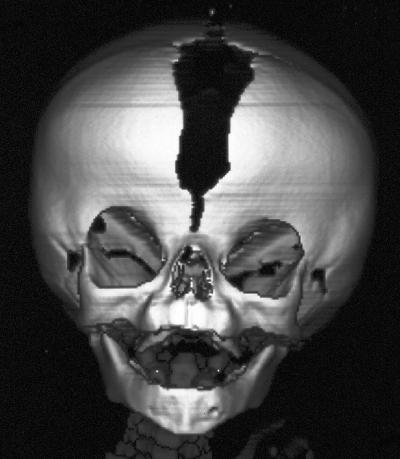
Cloverleaf skull is a trilobular skull with varying degrees of severity with different patients having different sutures involved (Cohen, 2000). Synostosis may involve the coronal, lambdoid, and metopic sutures.
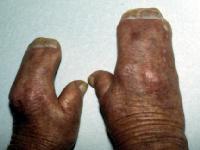
Apert syndrome is characterized by craniosynostosis, midface hypoplasia, and symmetric syndactyly. The skull is hyperacrobrachycephalic. The forehead is steep, wide and flat and the occiput is flat. Additionally the skull is wide and bulges at the temporal region (Cohen and Kreiborg, 1996). Apert syndrome is an autosomal dominant trait caused by a mutation in a gene called fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) (Cohen, 2000b). This mutation can be inherited from a parent or result in spontaneous mutilation during development. Prevalence is 15.5 in 1,000,000.
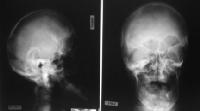
Crouzon syndrome is characterized by craniosynostosis, maxillary hypoplasia, shallow orbits and ocular proptosis. Cranial deformity depends on progression and order of synostosis; brachycephaly is most common but scaphocephaly, trigonocephaly and cloverleaf skull do occur (Cohen, 2000c). This too is an autosomal dominant trait caused by a mutation at FGFR2. Its prevalence is 15 to 16 per 1,000,000 and accounts for 4.5% of all cases of craniosynostosis (Cohen and Kreiborg, 1992).