Current Fuel Sources
Alternative Fuel Sources
References
Alternative Fuel Sources
- Nuclear
- Hydroelectric
- Biomass
- Geothermal
- Solar
- Wind

(Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, former USSR; http://www.chernobyl.co.uk/)
Nuclear energy provides
7.6% of the US energy needs. The primary sources that are used to
produce a nuclear reaction are Uranium-235 and Plutonium-239.
Nuclear energy is generated by the splitting of the nucleus of an atom,
called nuclear fission. When the nucleus divides energy is
released in the form of heat and light. Nuclear fission provides
a vast amount of energy, that when released slowly, can be harnessed to
produce electricity. The fission of an atom of uranium liberates
about 10 million times as much energy as the combustion of an atom of
carbon from coal.
Disadvantages:
Some of the
disadvantages to nuclear power plants are that they are relatively
expensive to construct and maintain, they produce hazardous nuclear
waste, and there is the potential for enormous nuclear disasters.
The waste produced from a nuclear reaction is highly toxic and can not
be recycled. It has to be stored in a secured location where it
will not effect the environment. The largest concern about
nuclear energy, however, is the possibility of a nuclear
disaster. One such disaster occurred at the Chernobyl nuclear
power plant in the former USSR.
On April 26th, 1986,
the Chernobyl nuclear power plant's number four reactor exploded,
sending a radioactive cloud across much of Europe. Following the
explosion, radioactivity with an intensity equivalent to 500 of the
bombs that destroyed Hiroshima at the end of World War II was measured
in the atmosphere. According to unofficial statistics, at least 15,000
people have died as a direct result of the explosion. The power station
is still seen by critics as a time bomb, and work has been carried out
ever since to try and make the site safe.
Hydroelectric Energy
Hydroelectric energy
provides roughly 3.8% of the US energy needs. It is currently the
largest source of renewable energy. Hydroelectric energy is a
very efficient source of energy and does not release any greenhouse
gases. Electricity is generated by water flowing downhill and
turning the blades of turbines. The three types of hydroelectric
energy generators are impoundment, diversion, and pumped storage.
An impoundment generator is when a dam is built to contain and direct
the flow of water to spin the turbines. A diversion hydroelectric
energy generator is when a channel is constructed to divert part of a
river to flow downhill through a turbine. Pumped storage
generators actually pump water back uphill so that it can be stored as
potential energy to be used later.
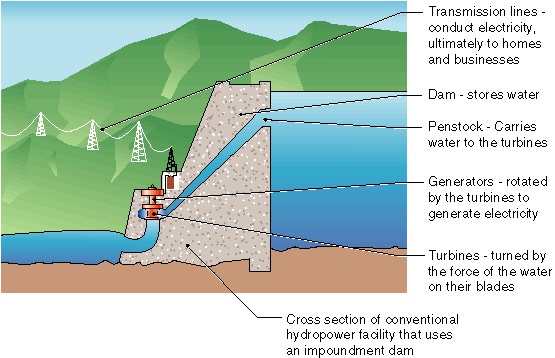
Disadvantages:
In order to harness
this large source of energy, dams and turbines must be
constructed. The construction of dams floods the area of land
upstream, thus greatly altering the surrounding ecosystem.
Biomass Energy

(A common landfill; http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/solar.renewables/page/mswaste/msw.html)
Biomass energy provides
3.2% of the energy used by the US. Biomass energy is organic
matter, many of which are waste products, that are used as fuel
sources. There are many different types of sources of biomass
energy that can be used such as: wood,
plants, residue from agriculture or forestry, and the organic component
of municipal and industrial wastes. Many biomass energy sources
can be converted directly into liquid fuels for our transportation
needs. Today, wood is still are largest biomass energy resource.
| Table B6. Average Heat Content of Selected Biomass Fuels | ||
| Fuel Type |
Heat Content
|
Units
|
|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Byproducts | 8.248 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Black Liquor | 11.758 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Digester Gas | 0.619 | Million Btu/Thousand Cubic Feet |
| Landfill Gas | 0.490 | Million Btu/Thousand Cubic Feet |
| Methane | 0.841 | Million Btu/Thousand Cubic Feet |
| Municipal Solid Waste | 9.945 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Paper Pellets | 13.029 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Peat | 8.000 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Railroad Ties | 12.618 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Sludge Waste | 7.512 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Sludge Wood | 10.071 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Solid Byproducts | 25.830 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Spent Sulfite Liquor | 12.720 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Tires | 26.865 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Utility Poles | 12.500 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Waste Alcohol | 3.800 | Million Btu/Barrel |
| Wood/Wood Waste | 9.961 | Million Btu/Short Ton |
| Source: Energy Information Administration, Form EIA-860B (1999), "Annual Electric Generator Report - Nonutility 1999." | ||
Disadvantages:
Biomass energy is not the cleanest source of energy. Most biomass sources are waste products that are not used, many of which produce a considerable amount of greenhouse gases.
Geothermal Energy

(Geothermal energy pumps; http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/solar.renewables/page/heatpumps/heatpumps.html)
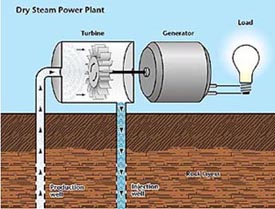
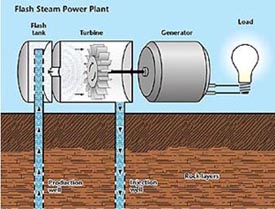
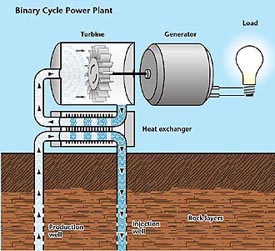
Geothermal energy can only be used in areas where reservoirs are found in geothermal systems, which are regionally localized geologic settings, where the Earth's naturally occurring heat flow is near enough to the Earth’s surface to bring steam or hot water to the surface. Thus, geothermal energy can not meet every energy need. Also, geothermal energy produces only a small amount of electricity compared to other alternative fuel sources.
Solar Energy
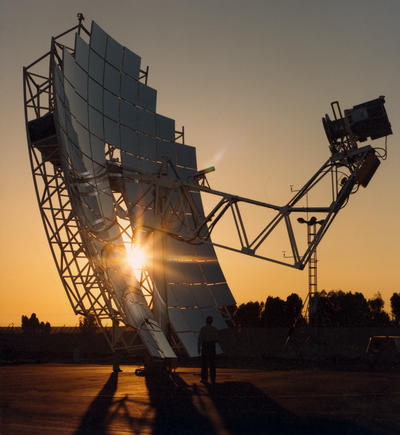

(http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/solar.renewables/page/solarthermal/solarthermal.html)
Disadvantages:
The main disadvantage of solar energy is its limited time of use. It is not an efficient energy source at night or during overcast days. The amount of electricity produced by solar energy depends on the amount of light emitted by the sun. If the light emissions are obstructed from reaching the photovoltaic receptors, no electricity is generated. Also, solar energy is seasonally dependent. More sunlight reaches the Earth during the summer months then the winter months because of longer daylight. So solar energy is not as efficient during the winter.
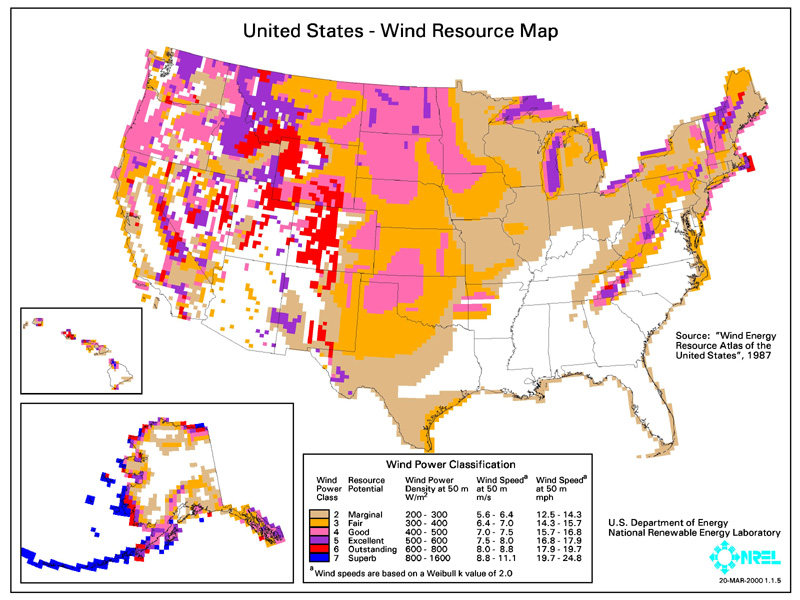
Wind Energy

(http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/solar.renewables/page/wind/wind.html)
Disadvantages:
The main disadvantage of wind energy is that good wind sites are in remote locations. These sites are often situated miles away from the citys that could use the electricity. Long stretches of power lines are needed to connect each city to the wind energy generators.