Current Fuel Sources

(http://www.umich.edu/~gs265/society/fossilfuels.htm)
The three main fossil fuels the
United States relies on to meet the current energy requirements
are: Oil, Natural Gas, and Coal. Fossil fuels are
hydrocarbon based natural resources that were formed over 300 hundred
millions of years ago by the fossilization of prehistoric plants and
animals. We have learned to harness the energy released from
these fossil fuels during combustion in order to meet our energy
needs. Fossil fuels are a common source of energy we use
everyday. They are used to generate the electricity that runs our
household appliances, fuel the motors of our cars, and heat our
homes. Fossil fuels are currently essential to providing the
energy needs of our everyday lives. This, however, is a subject
of some concern.
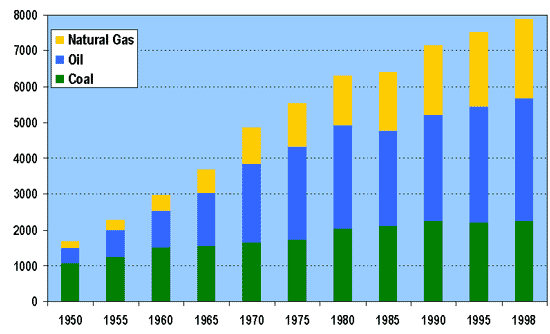
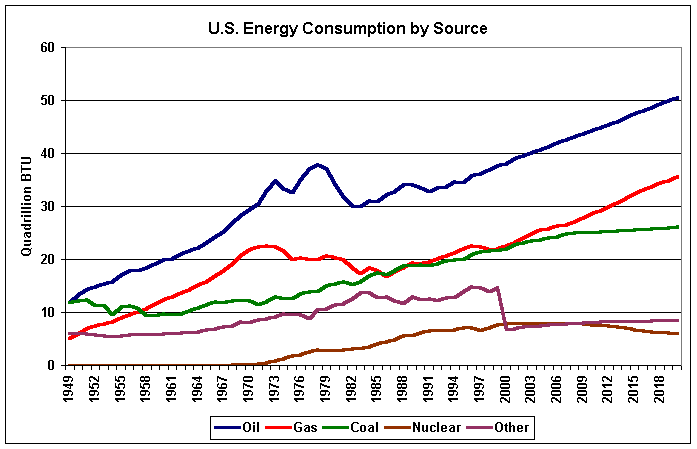
Fossil fuels are
depleting at an alarming rate. They are a
nonrenewable resource and we are consuming vast quantities of them
every day. Varying estimates project a complete depletion of oil
and natural gas within anywhere from 40-100 years.
Coal is the most abundant of the three and will last for about
another 230 years. It is very likely that
within our life times that one of these fossil fuels, if not more, will
be completely consumed from the planet.

•
US dependency on fossil fuel energy as a percentage of total energy consumption:
US dependency on fossil fuel energy as a percentage of total energy consumption:
<>Oil
<>38.8%
<>Natural Gas
<>23.2%
<>Coal
<>22.9%
<>
<><>Natural Gas
<>23.2%
<>Coal
<>22.9%
<>

“Fossil fuels – coal, oil and natural gas
-- currently provide more
than 85% of all the energy consumed in the United States, nearly two-thirds of
our electricity, and
virtually all of our transportation fuels. Moreover, it is likely
that the nation’s reliance on
fossil fuels to power an expanding economy will actually increase over at least the next
two decades even with
aggressive development and deployment of new renewable and nuclear technologies.”
-US
Department of Energy
The Effects on Global Warming:
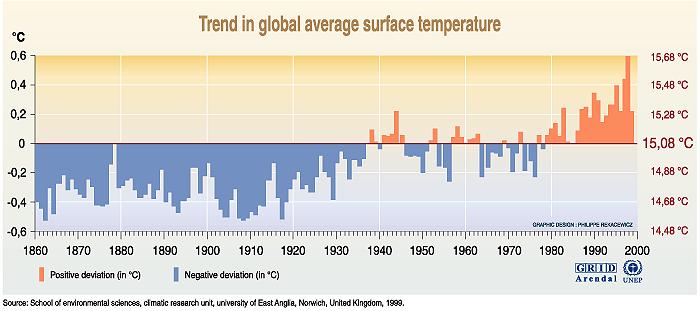
The Effects on Global Warming:

The main drawback of fossil fuels
is the vast quantities of pollution produced from burning them.
Burning any fossil fuel produces carbon dioxide, which adds to the
green house effect, thus warming the Earth. As you can see from
the graph displayed above, the average surface temperature of the Earth
has been increasing rather rapidly in the past 20 years. Global
warming is directly associated with the increase in greenhouse gases
produced from the burning of fossil fuels.