
 www.ilizarov.org/
www.ilizarov.org/Treatments and Procedures
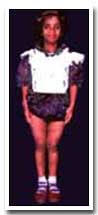
Tibial Lengthening and 3 years post surgery
A whole-body x-ray should be taken because diagnostic precision is essential for predicting prognosis and radiographic changes might occur. Prenatal diagnosis is possible in some cases (when fetal limb shortening is severe). Standard laboratory tests do not help in diagnosing osteochondrodysplasias, but molecular diagnosis is available for Achondroplasia and disorders associated with defects in the diastrophic dysplasia sulfate transporter (DTDST) gene. This gene encodes a transmembrane protein that transports sulfate into chondrocytes and mutations in this gene are responsible for four recessively inherited Chondrodysplasias.
For some nonlethal types, surgery may help improve function. In osteochondrodysplasia, it is common for the knees to touch and the ankles to be separated by a good distance; this is called Genu valgum or "knock knees." If the deformity is greater than 20 degrees, treatment by realignment osteotomy (dividing of a bone) is offered. If polydactyly is present then surgical treatment is provided usually between 6 mo.-1 yr. Hypoplasia of the odontoid process can cause the compression of the spinal cord. Therefore, the odontoid process should be evaluated preoperatively, and if it is abnormal, the patient's head should be carefully supported when hyperextended.
Also because the inheritance pattern in most types is known, genetic counseling can be effective. In the US there are organizations, such as Little People of America, that help provide resources for affected people and are supporters on their behalf.