What is
Ankylosing Spondylitis?
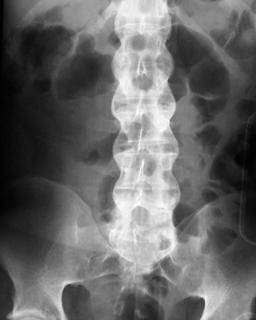
Ankylosing Spondylitis
(AS) is one of the many forms of spondyloarthropathy or spondyloarthritis, and
more specifically, a seronegative auto-immune spondyloarthropathy. AS is a
chronic, progressive, inflammatory arthritis affecting the spine primarily,
with involvement of other joints as well, especially the sacroiliac (SA) joint.
It typically affects males (5:1) between 15 and 35 years of age, though
children as young as 3 can show signs (Roberts and Manchester 158). The exact etiology
is not clear though the gene HLA-B27 appears to have a primary role in AS and
other seronegative spondyloarthropathies. 90-95% of AS patients test positive
for HLA-B27, but not everyone with the gene develops AS (Roberts and Manchester 158). AS is seen more
commonly in Caucasians and Native American populations and rarely in African
Americans and Japanese.
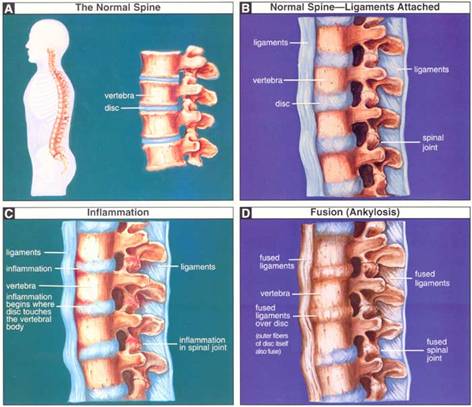
Process
of Fusion
-Inflammation of SA joints, unilateral
or bilateral, followed by ankylosis
-Inflammation of intervertebral joints
-Healing of fibrous tissue produces
calcification that ankyloses the synovial (apophyseal and costovertebral) joints
of the spine
-Interspinous and superspinous ligaments
also ossify, progressing from lumbar spine up
-Formation of bony syndesmophytes further
fuse vertebrae
-Outer margins of fibrous intervertebral
discs ossify