Theories
explaining the association of HLA-B27 and 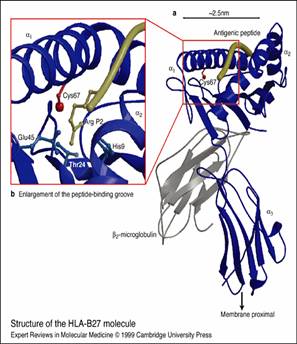 Spondyloarthropathies (Bowness
858)
Spondyloarthropathies (Bowness
858)
-HLA-B27 is in genetic
linkage with a disease associated gene
-HLA-B27 binds and
presents ‘arthritogenic’ peptides to T cells
-HLA-B27 is involved thymic selection of a T-cell repertoire that is susceptible
to spondyloarthritis
-HLA-B27 has an unusual
cell biology compared with other HLA
class 1 molecules
-The
HLA-B27 free cysteine at position 67 can be modified, leading to an ‘altered self’
-There is cross reactivity between antibodies directed at bacterial protein(s) and HLA-B27
-HLA-B27
is a receptor for a bacterial ligand
-Interaction of HLA-B27 with a bacterial superantigen
causes non-specific T-cell stimulation
-HLA-B27-derived
peptides are presented by HLA class 2 (6) molecules to CD4+ T cells