The main effect of acid rain
on Earth is on the water ecosystems. The acidification of lakes and
streams in North America is an increasingly dangerous problem not only
for the life in the waters, but also for humans who depend on the marine
life for food and the water to drink. Acidification usually occurs
in sensitive bodies of water. These sensitive waters rest atop soil
with a limited ability to neutralize acidic compounds. In other words,
they have a low buffering capacity.
As water pH approaches six, crustacean, insects, and plankton begin to
die. At a pH of five, major changes in the plankton composition take
place causing everything to be disrupted. Below a pH of five, water
is largely devoid of any fish.
Throughout the process of acidification by the acid rain, the entire predator/prey
relationship is detrimentally affected.
In North America, the effects
of acid rain can be seen in numerous areas. A condition known as
chronic acidity in which a body of water has a constantly low pH exists
in many lakes and streams. An estimated 14,000 Canadian lakes are
acidic due to the factories in both eastern Canada and several states in
the United States. These lakes have lost significant numbers of fish,
and over 300,000 more are now vulnerable to acid deposition. Another
important effect of the acid rain in Canada is on the Atlantic salmon catch,
which has substantially declined since the 1950's. In the United
States, the acid rain is also a problem in the east where
pH levels of
rain are relatively low due to the numerous factories. Hundreds of
lakes in the Adirondack Park and Mountains in New York are unsuitable for
sensitive fish species. The highest rate of acidic streams in the nation,
more than 90%, exists in the New Jersey Pine Barrens. Over 1350 streams
in the Mid Atlantic Highlands are also acidic. The acidification
problem grows when episodic acidification is taken into account.
This phenomena occurs from snow melting or heavy downpours and can cause
large scale "fish kills". A final detrimental effect of acid rain
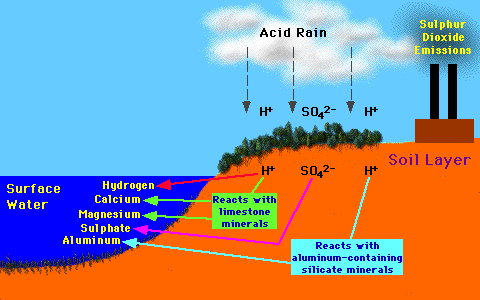
on bodies of water occurs through the reaction of the acid rain with the
soil, specifically the limestone and aluminum containing silicate minerals.
This can cause certain harmful materials to seep into the water, disrupting
marine life.