

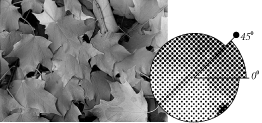
Halftone screens and duotones



Halftone process
Types of screens
Newspapers - 60-85
line screens;
Magazines and catalogs -
130-150
Laser 300 and above
The finer the screen, the
closer together the dots
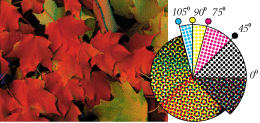
Color separations

Color -- What separations consist of:
Additive & Subtractive colors
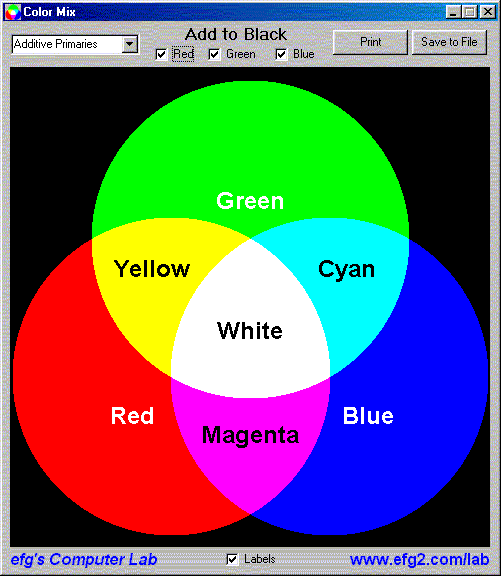
RGB
color is all around us in the form of light, and is referred to as
the
Additive color system.
On our projector in class, Red, Green and Blue filters are placed in front
of high powered spot lights
and the three lights directed to the same surface, which produces
overlapping; a white
area would appear where ALL three lights overlap.
Where each light overlaps another we would see Cyan, Magenta or Yellow
- the Subtractive color
system components.
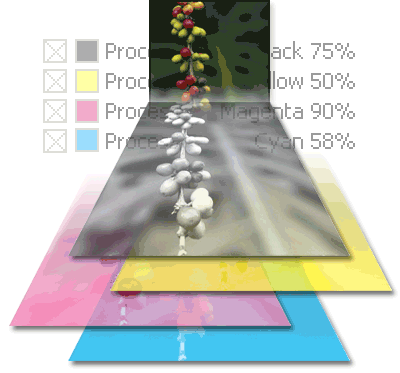
How Color gets printed:
Because
CMY cannot produce Black we must add a fourth pigment to assist many colours
reproduced
on a press and make the application of 100% of CMY appear black. This fourth
colour is
indeed Black
- often referred to as the KEY colour, hence the CMYK printing
process.
CMY
and K values can be 0% for none (white) to 100% for full colour (percentage
halftone dot size).
Colors
can be described from/to anywhere in the world by using one of several
color reference
systems:

Pantone Matching System - PMS spot color vs process color
Bitmaps and channels
Bit
is the basic and minimum value used by or referenced in a computer at both
the electronic and
software level. (Notice your file size references that may be 104Kb (example)
or 104 thousand Bytes
where a Byte = 8 Bits). Therefore a Bitmap is a map or organised array
of pixels of Bit based
information.
• Black and White images have only one CHANNEL.
• Greyscale images also have only one CHANNEL.
• RGB images have three CHANNELS.
CMYK
CMYK Bitmapped images present quite a different story although you've probably
already guessed
that they have four CHANNELS, and are referred to as 32Bit Bitmaps - 8Bits
(C) + 8Bits (M) + 8Bits
(Y) + 8Bits (K) = 32 Bits.
Ink and Paper affects the result
CMY
pigments are far from perfect.
The
different bases that they are transferred to also differ greatly (even white
paper is not all the
same and can
produce varying results). The best CMY pigments that man can produce contain
elements of the
other two colours - they do not absorb/reflect light perfectly.
Black doesn't exist
We cannot separate black, it has to be constructed once the RGB to CMY results are established.
There just aren't enough colors
Finally
consider that we can only reproduce 10 or 11 million colors with CMYK processes.
A 32Bit CMYK 4 channel bitmapped image therefore only maps the restricted number
of reproducible colors.
Color Theory exercise:
1. Find three colors that you like using Color SchemerColor Schemer and make a logo in PageMaker using your name.